You are browsing the docs for Nexus v1.6.x, the latest release is available here
API Reference
Nexus Delta exposes a RESTful interface over HTTP(S) for synchronous communication. The generally adopted transport format is JSON based, specifically JSON-LD. However, other response formats are supported through Content-Negotiation
The API provides access and management of several primary resource types.
Identities
Identities endpoint can be used to fetch user identities.
Permissions
A permission is the basic unit to provide a way to limit applications’ access to sensitive information.
Realms
A realm provides with the necessary information to perform authentication against a certain OIDC provider .
ACLs
In order to restrict applications’ access to data by placing restrictions on them, three parameters are important:
- permission: the value used to limit a client (user, group) access to resources.
- identity: a client identity reference, e.g. a certain user, a group, an anonymous user or someone who is authenticated to a certain realm.
- path: the location where to apply the restrictions
An ACL defines the set of permissions that certain identities have on a concrete path.
Organizations
The top-level grouping resource in the platform, called organization
Projects
The 2nd level grouping resources in the platform, called project. Projects provide isolation of ACLs, resource resolution and indices (ElasticSearch index and Blazegraph namespace).
Quotas
Defines the maximum number of resources and events that can exist in a certain scope.
Schemas
A schema is a resource which defines a set of rules and constrains using SHACL.
Resources
A resource is the most generic entity on the Knowledge Graph. Resources can be schemas, resolvers, views, storages, files or data.
Resolvers
A resolver is a resource which defines the way ids are retrieved inside a project.
Views
A view is a resource which defines the way indexing is applied to certain resources inside a project.
Storages
A storage is a resource which represents a backend where files are stored. It describes where and how files are created and retrieve.
Files
A file is a binary attachment resource.
Archives
An archive is a collection of resources stored inside an archive file. The archiving format chosen for this purpose is tar (or tarball).
Resource Lifecycle
Nexus Delta is build using the event sourcing approach. This strategy captures all changes to an application state as a sequence of events.
All resources in the system generally follow the very same lifecycle, as depicted in the diagram below. Every interaction with an API resource (creation, updates, state changes) is recorded into the system as revisions.
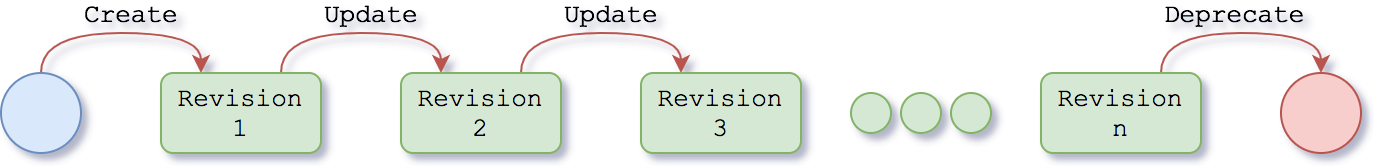
Data is never removed from the system, but rather is marked as deprecated. Depending on the type of resource, the deprecation flag may have various semantics:
- Organizations: the resource itself and sub-resources cannot be updated. Views and resolvers contained within this organization will not be considered during indexing and resolution processes.
- Projects: the resource itself and sub-resources cannot be updated. Views and resolvers contained within this project will not be considered during indexing and resolution processes.
- Schemas: the resource itself cannot be updated and new data conformant to it cannot be created
- Resolvers: the resource itself will not be considered during the resolution process
- Views: the resource itself will not be considered during the indexing process
- Storages: no new files can be created against the deprecated storage
- Files: attachments cannot be added/deleted
- Data: the resource itself cannot be updated
Archives resources are an exception. Those resources are ephemeral. They will be automatically removed from the system after certain time. This time is configurable (config property app.archives.cache-invalidate-after) and it defaults to 5 hours.
Future policies may use this flag to determine if or when the deprecated data may be archived.